Enhanced comment feature has been enabled for all readers including those not logged in. Click on the Discussion tab (top left) to add or reply to discussions.
Genetic Evaluation: Difference between revisions
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===BLUP=== | ===BLUP=== | ||
===ssGBLUP (Suggested writer: Daniela Lourenco)=== | ===ssGBLUP (Suggested writer: Daniela Lourenco)=== | ||
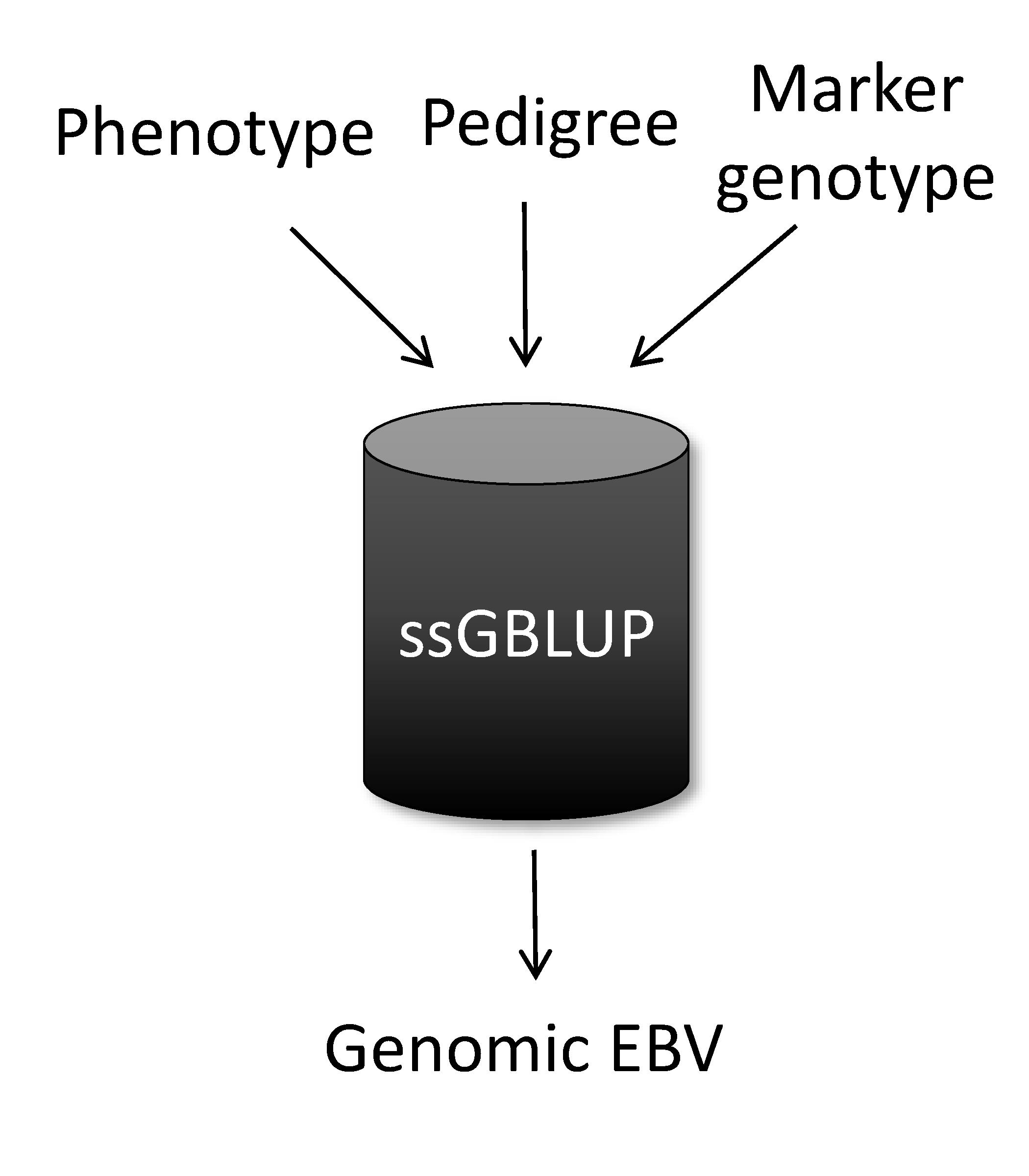
Single-step genomic BLUP (ssGBLUP) <ref> Legarra, A., I. Aguilar, and I. Misztal. 2009. A relationship matrix including full pedigree and genomic information. J. Dairy Sci. 92:4656-4663. </ref><ref> Aguilar, I., I. Misztal, D. L. Johnson, A. Legarra, S. Tsuruta, and T. J. Lawlor. 2010. Hot topic: A unified approach to utilize phenotypic, full pedigree, and genomic information for genetic evaluation of Holstein final score. Journal of Dairy Science 93: 743-752. </ref> is a method developed to enable the inclusion of maker genotypes into the well-known BLUP machinery. The idea of ssGBLUP came from the fact that only a small portion of the animals in the pedigree is genotyped. In this way, one approach to account for all animals (i.e., genotyped and non-genotyped) in the evaluation would be to combine pedigree and genomic relationships and use this as the covariance structure in the BLUP mixed model equations. Thus, ssGBLUP uses marker information to construct genomic relationships. | |||
Legarra et al. (2009)<ref> Legarra, A., I. Aguilar, and I. Misztal. 2009. A relationship matrix including full pedigree and genomic information. J. Dairy Sci. 92:4656-4663. </ref> stated that genomic evaluations would be simpler if genomic relationships were available for all animals in the model. Then, their idea was to look at the pedigree relationship as a priori relationship and at the genomic relationship as the observed relationship. Based on that, they showed the genomic information could be extended (i.e., imputed) to non-genotyped animals. This means that in ssGBLUP pedigree relationships for non-genotyped animals are enhanced by the genomic information of their relatives. As a result, the output of ssGBLUP for each animal is automatically a genomic EBV. | |||
<center> | |||
[[File:figure1_ssGBLUP.jpg]] | |||
</center> | |||
===[[Single-step Hybrid Marker Effects Models]] (Suggested writer: Bruce Golden)=== | ===[[Single-step Hybrid Marker Effects Models]] (Suggested writer: Bruce Golden)=== | ||
Revision as of 18:12, 1 February 2019
EPD
Utility (compared to actual/adjusted phenotypes, ratios, disjoined marker scores, etc.) (Suggested writer: Megan Rolf)
Basic Models
BLUP
ssGBLUP (Suggested writer: Daniela Lourenco)
Single-step genomic BLUP (ssGBLUP) [1][2] is a method developed to enable the inclusion of maker genotypes into the well-known BLUP machinery. The idea of ssGBLUP came from the fact that only a small portion of the animals in the pedigree is genotyped. In this way, one approach to account for all animals (i.e., genotyped and non-genotyped) in the evaluation would be to combine pedigree and genomic relationships and use this as the covariance structure in the BLUP mixed model equations. Thus, ssGBLUP uses marker information to construct genomic relationships.
Legarra et al. (2009)[3] stated that genomic evaluations would be simpler if genomic relationships were available for all animals in the model. Then, their idea was to look at the pedigree relationship as a priori relationship and at the genomic relationship as the observed relationship. Based on that, they showed the genomic information could be extended (i.e., imputed) to non-genotyped animals. This means that in ssGBLUP pedigree relationships for non-genotyped animals are enhanced by the genomic information of their relatives. As a result, the output of ssGBLUP for each animal is automatically a genomic EBV.
Single-step Hybrid Marker Effects Models (Suggested writer: Bruce Golden)
Interim Calculations
Bias
(in)complete reporting / contemporary groups / preferential treatment (Suggested writer: Bob Weaber
Accuracy (Suggested writer: Matt Spangler)
meaning of accuracy
what impacts accuracy
different definitions of accuracy (true, BIF, reliability)
Variance components (Suggested writer: Steve Kachman)
Impact on EPD, accuracy, genetic gain (Suggested writer: Steve Kachman)
Heterogeneous variance
Connectivity (Suggested writer: Ron Lewis)
Measures of (Suggested writer: Ron Lewis)
==Impact on GE== (Suggested Writer: Ron Lewis)
Current GE
How each breed (organization) is modeling each trait (Suggested writers: Steve Miller, Lauren Hyde, AHA)
- ↑ Legarra, A., I. Aguilar, and I. Misztal. 2009. A relationship matrix including full pedigree and genomic information. J. Dairy Sci. 92:4656-4663.
- ↑ Aguilar, I., I. Misztal, D. L. Johnson, A. Legarra, S. Tsuruta, and T. J. Lawlor. 2010. Hot topic: A unified approach to utilize phenotypic, full pedigree, and genomic information for genetic evaluation of Holstein final score. Journal of Dairy Science 93: 743-752.
- ↑ Legarra, A., I. Aguilar, and I. Misztal. 2009. A relationship matrix including full pedigree and genomic information. J. Dairy Sci. 92:4656-4663.